# The Crucial Role of Dendritic Cells in Your Immune Defense
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Dendritic Cells
Within your body lies an extraordinary cell that plays a vital role in your survival: the dendritic cell. This unique cell has a fascinating duty—constantly ingesting and processing materials from your body.
This paragraph will result in an indented block of text, typically used for quoting other text.
Section 1.1: The Function of Dendritic Cells
Dendritic cells are like the body’s sentinels, diligently patrolling for threats. When they encounter bacteria, they engulf these invaders and break them down into fragments. Subsequently, they present these bacterial pieces on their surface, akin to an octopus showcasing its tentacles.
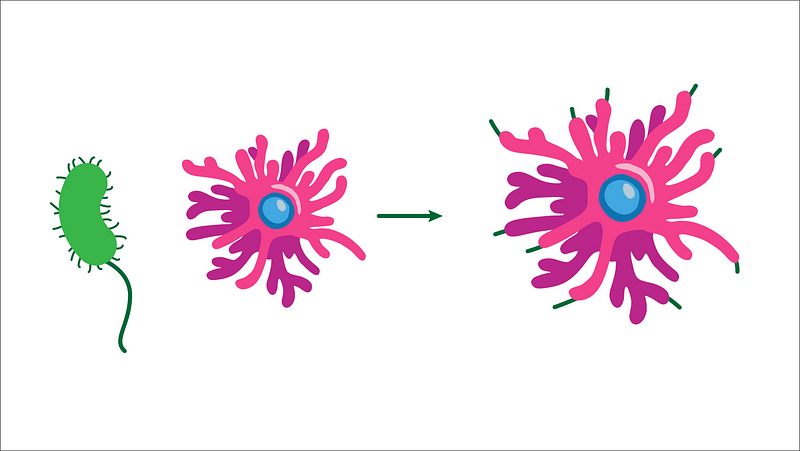
Once a dendritic cell identifies a bacterium, it ceases its intake process and seeks out T cells, which are crucial components of the Adaptive Immune System.
Section 1.2: What Are T Cells?
T cells are remarkable defenders that can adapt to a myriad of diseases, from the common cold to more severe ailments like Ebola. They are prepared to combat not only current pathogens but also future threats, even hypothetical ones that may emerge a million years from now.
The Inner Life of the Cell Animation - YouTube
This animation provides an insightful look into the intricate workings of cells, including dendritic and T cells, highlighting their roles in the immune response.
Chapter 2: The Journey to Activation
Dendritic cells navigate to the lymph nodes, where T cells reside. The lymphatic system acts as a filtration system for fluids leaking from blood vessels, and it is here that dendritic cells present the bacterial fragments to specific T cells.
Section 2.1: The Activation Process
When dendritic cells encounter the right T cell, they bind seamlessly, triggering T cell activation. They also release signaling molecules to inform the T cells about the specific pathogen.
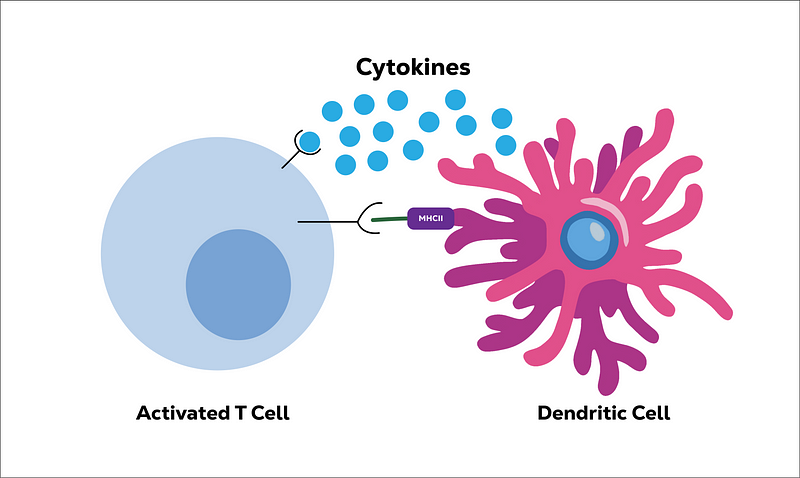
What happens once T cells are activated? They exhibit three key abilities that make them formidable defenders.
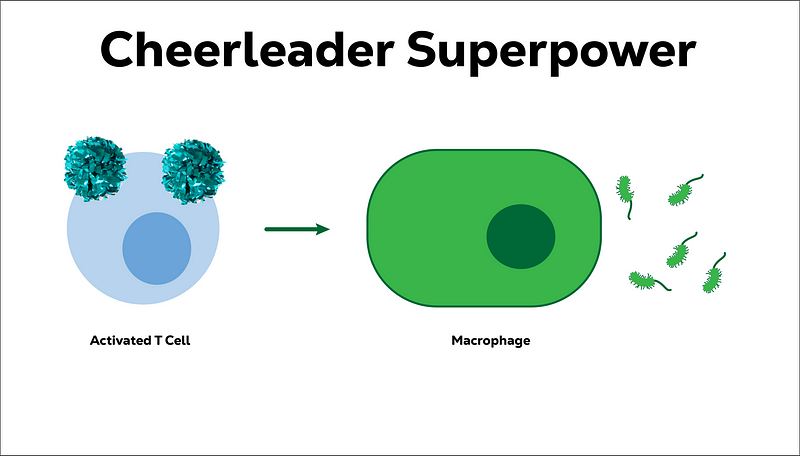
Subsection 2.1.1: The Cheerleader Effect
T cells take on the role of motivators, boosting the morale of other immune cells, particularly macrophages, during battles against intruders. Their encouragement helps revitalize tired cells, inspiring them to continue the fight.
Subsection 2.1.2: The Killer Mechanism
Some T cells, known as cytotoxic T cells, become highly aggressive and target bacteria with precision. Their accuracy ensures that surrounding healthy cells remain unharmed, making them akin to elite snipers within the immune system.
Subsection 2.1.3: The Antibody Brigade
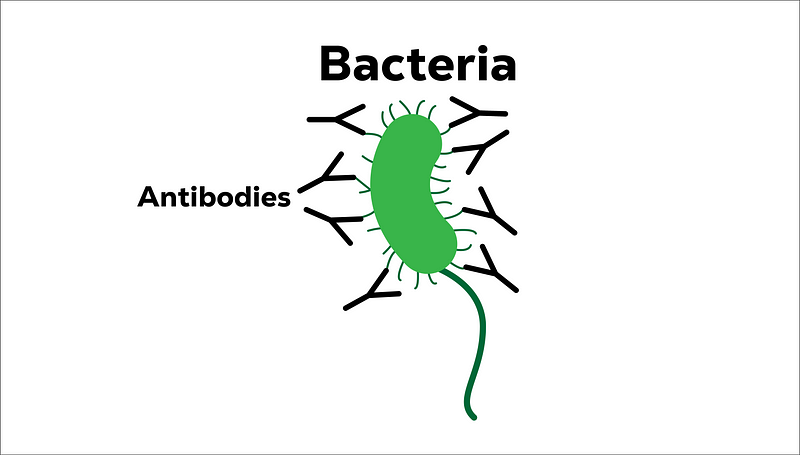
T cells also summon B cells, which are capable of producing millions of antibodies—Y-shaped proteins designed to immobilize and eliminate bacteria. These antibodies are essential for enhancing the immune response.
Despite their effectiveness, the process of dendritic cells locating their T cell counterparts can be time-consuming.
Chapter 3: The Memory Factor
Fortunately, T and B cells generate memory cells upon activation. These specialized cells allow for a faster and more efficient response to previously encountered pathogens, leading to immunity.
An Egg Is Just One Cell - YouTube
This video elucidates the concept of cellular biology, emphasizing the significance of various cell types, including those involved in the immune response.
The principle behind vaccinations leverages this memory mechanism by introducing harmless components of pathogens, effectively training the immune system without causing illness.
In conclusion, vaccines play a pivotal role in safeguarding not only individual health but also public health by curbing the spread of diseases. Vaccination efforts have been instrumental in eradicating diseases like smallpox, showcasing the power of the immune system in action.
As we continue to explore the intricacies of our immune defenses, the next discussion will delve into how our bodies prepare for future diseases.
This blog post draws inspiration from the book Immune by Philipp Dettmer, an excellent resource for anyone fascinated by the immune system. For further insights and updates, consider subscribing to my newsletter or supporting my work on Patreon.