Fascinating Insights into Technetium-99m in Medical Imaging
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Technetium-99m
You might not have come across the term Technetium-99m (Tc-99m) in your daily life, but its importance in the realm of medical imaging is truly remarkable. This radioactive isotope plays a crucial role in diagnosing various health conditions.
Here are five intriguing facts about this versatile isotope that you may not have known:
Section 1.1: The Production Process
Tc-99m is derived from its parent isotope, molybdenum-99 (Mo-99), which is generated in nuclear reactors. With a half-life of just 66 hours, Mo-99 must be swiftly transported to healthcare facilities to ensure its effective use in producing Tc-99m.
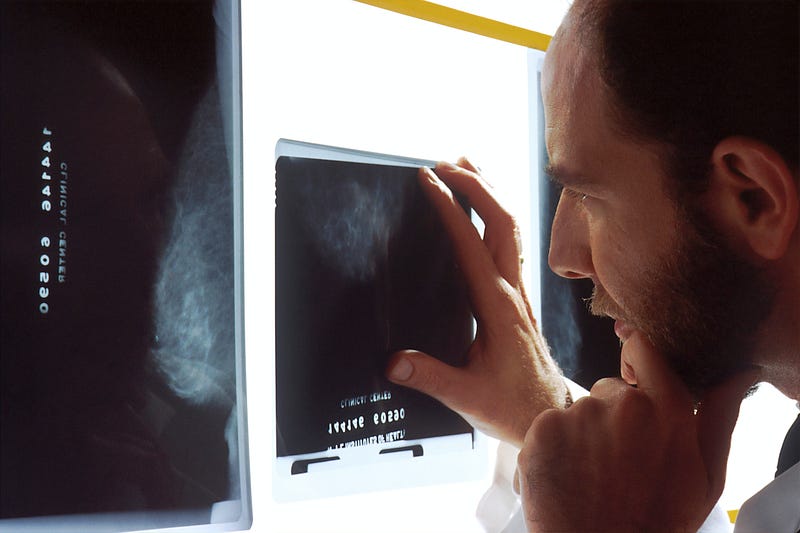
Section 1.2: Imaging Capabilities
Tc-99m emits gamma radiation detectable by specialized imaging devices known as gamma cameras. Upon injection into a patient's body, it helps create detailed images of organs and tissues, enabling healthcare providers to diagnose and monitor a wide array of medical issues.
Subsection 1.2.1: Short Half-Life Benefits
One of the significant advantages of Tc-99m is its brief half-life of approximately 6 hours. This rapid decay means that it does not linger in the body for extended periods, significantly reducing radiation exposure for patients.
Section 1.3: Versatile Applications
Tc-99m is integral to various imaging techniques, including bone scans, cardiac stress tests, and assessments of the brain, liver, lungs, and kidneys. Additionally, it aids in identifying cancerous tumors and tracking the effectiveness of cancer treatments.
Chapter 2: Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its extensive use, Tc-99m faces challenges. The production of Mo-99, essential for Tc-99m synthesis, heavily depends on nuclear reactors, which can be costly to operate and maintain.
In this video, titled "Technetium - Periodic Table of Videos," you will explore the significance of Technetium in the periodic table and its applications in various fields.
The next video, "#MyFaveElement: Technetium," provides personal insights into why Technetium is a favorite among enthusiasts, highlighting its unique properties.
Overall, Tc-99m has established itself as an indispensable asset in medical imaging. Its short half-life, ability to generate high-resolution images, and minimal radiation exposure make it a preferred option for numerous diagnostic procedures. Nevertheless, continuous advancements in the production and distribution of Mo-99 will be vital to ensuring that Tc-99m remains accessible to healthcare professionals.