Revolutionizing Medical Trials: Prioritizing Safety in Research
Written on
Chapter 1: The Shift in Clinical Trials
In the realm of medical research, the focus has often been on big data. However, a transformative approach is gaining attention by championing the significance of small sample trials. This method emphasizes safety rather than just efficacy, addressing pivotal questions about the reasoning behind trial outcomes through precise finite sample likelihood and statistical decision theory. By thoroughly examining data from trials involving as few as two to fifty participants, researchers have formulated decision-making rules that can surpass conventional techniques reliant on the Boole-Fréchet-Hoeffding bounds. This methodology not only promotes safer medical interventions but also clarifies the inconsistencies that can arise in clinical trial results, ultimately redefining experimental practices in healthcare.
Safety in Clinical Trials | PrepRARE Webinar - YouTube
This video discusses the critical need for safety in clinical trials, showcasing how prioritizing patient well-being can reshape research methodologies.
Section 1.1: Embracing Bayesian Decision-Making
At the core of this progressive strategy lies Bayesian decision-making. Unlike traditional methods that may neglect the intricacies of small sample sizes, Bayesian approaches utilize exact finite sample likelihood to yield more precise predictions. When applied to actual clinical trials, such as those assessing high-dose Vitamin C for sepsis patients, researchers are equipped to make more informed choices that focus on patient safety. This not only bolsters the trustworthiness of trial results but also offers a solid framework for interpreting mixed findings in subsequent research. The shift toward Bayesian techniques marks a substantial advancement in the pursuit of safer and more effective medical treatments.
Subsection 1.1.1: Balancing Efficacy and Safety
The most intriguing aspect of this novel method is its emphasis on the fine line between efficacy and safety. Traditional clinical trials frequently prioritize effectiveness, sometimes at the risk of participant safety. By integrating a utility function that favors safety, researchers can engage in more ethical decision-making. This is especially vital in early-phase trials, where the primary objective is to ensure that new treatments do not endanger participants. By reassessing previous trials with these new decision frameworks, researchers can uncover valuable insights into why certain treatments may have failed and how future studies can be enhanced.
Chapter 2: Insights from High-Dose Vitamin C Trials
The application of these innovative decision frameworks to a clinical trial involving high-dose Vitamin C for sepsis patients yielded compelling insights. Initial findings indicated a notable decrease in 28-day mortality, yet subsequent larger trials resulted in mixed results. By re-evaluating the data through finite sample Bayesian and maximum likelihood principles, researchers identified that while the treatment was beneficial for some, it posed risks for others. This nuanced understanding underscores the necessity of considering both efficacy and safety in clinical research.
Why Clinical Trials Must Prioritize Patient Safety Over Data | Risk Mitigation Insights
This video explores the crucial need for prioritizing patient safety in clinical trials, emphasizing how data should never come at the expense of well-being.
Section 2.1: The Importance of Safety-First Trials
The re-analysis of high-dose Vitamin C trials for sepsis patients, utilizing the new decision-making rules, revealed that while effective for some individuals, the intervention could be unsafe for others. This vital insight highlights the importance of balancing efficacy with safety in clinical trials. As we refine these methodologies, the potential to revolutionize medical research and enhance patient outcomes becomes increasingly evident.
Outcomes of High-Dose Vitamin C Trials for Sepsis Patients
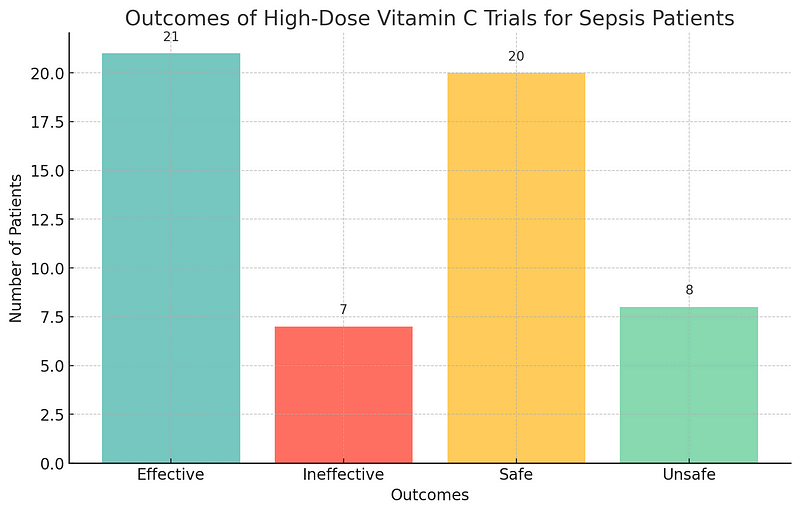
Graph depicting the efficacy and safety balance of high-dose Vitamin C trials for sepsis patients. The visualization highlights effective and ineffective treatments, as well as safe and unsafe outcomes.
Conclusion: A Transformative Era in Medical Research
By prioritizing safety over efficacy, small sample trials utilizing exact finite sample likelihood have demonstrated superior performance compared to traditional methods, ensuring safer medical interventions and more reliable trial results. The implementation of Bayesian decision-making techniques enhances predictive accuracy, particularly in small sample studies where conventional methods may struggle. The application of these innovative techniques to early-phase trials is crucial for ensuring participant safety, transforming medical research and significantly improving patient outcomes. As we stand on the brink of a new era in medical research, the emphasis on patient safety promises to foster groundbreaking discoveries and inspire future generations of scientists.