The Jet Stream: Unraveling the Mystery of Earth's Fastest Winds
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding the Jet Stream
The jet stream represents the fastest winds in the atmosphere and plays a crucial role in global weather patterns. Airlines utilize the jet stream to enhance flight efficiency, as its winds can either accelerate or decelerate aircraft based on their direction.

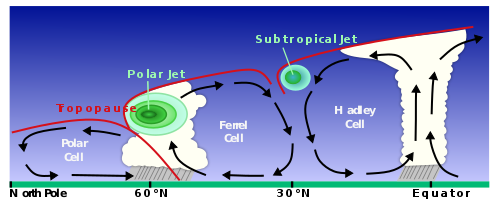
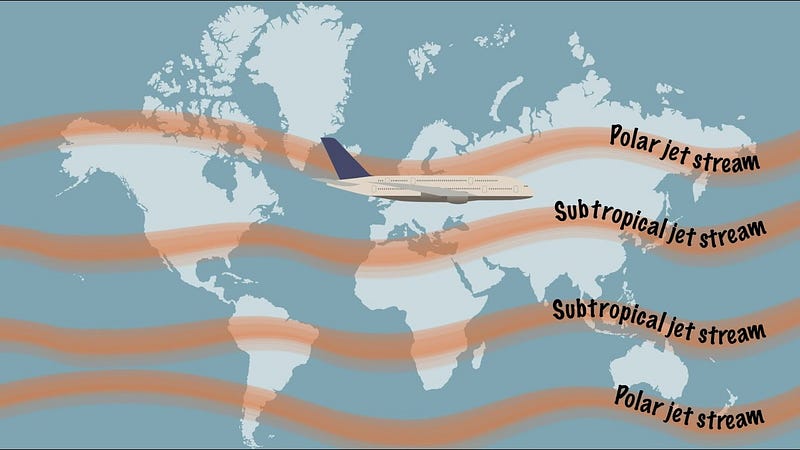
The jet stream occurs worldwide, forming when temperature disparities between air masses reach approximately 30 degrees Celsius. Typically situated at altitudes between 9 to 16 kilometers (30,000 to 52,000 feet), these winds can reach average speeds of 160 to 240 km/h (150 mph), with peaks of over 400 km/h (250 mph) at times. This narrow band of winds usually spans a few hundred kilometers in width, divided into two primary streams: the subtropical jet stream around 30 degrees latitude and the polar jet stream at approximately 60 degrees latitude. The jet stream's position fluctuates with the seasons, shifting southward in winter and northward during summer in the Northern Hemisphere.
Section 1.1: Mechanisms Behind the Jet Stream
The largest jet streams can be found in both the northern and southern hemispheres. These fast winds develop in the upper troposphere, above the lower atmosphere, primarily due to temperature contrasts between high-altitude air masses. When warm and cold air masses converge at frontal boundaries, atmospheric conflicts arise, producing powerful winds. The Coriolis effect, resulting from the Earth's rotation, causes winds to veer to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere, thus generating rapid winds along these boundaries. Consequently, the jet stream adapts and transforms shape in response to fluctuations in temperature and atmospheric pressure.
Subsection 1.1.1: Benefits of Understanding the Jet Stream
The jet stream was first documented by aviators in the 1920s and 1930s. One key advantage of the jet stream lies in its ability to enable commercial airliners to travel faster at high altitudes, thereby saving time and fuel, which leads to reduced travel costs. Additionally, with insights into wind patterns, wind turbines positioned at high altitudes can harness energy more effectively. The jet stream also significantly impacts surface weather conditions, influencing storm formation and various weather systems. Understanding these wind patterns assists farmers in crop planning, predicting droughts or heavy rainfall, and managing water resources efficiently. Researchers continue to study the jet stream to gain insights into its role in weather phenomena and climatic shifts, including connections to El Niño and La Niña.
Chapter 2: The Consequences of a Slowing Jet Stream
The term "jet stream" was first coined in 1939 by Japanese meteorologist Wasaburo Ooishi. A slowdown or potential disappearance of the jet stream could have profound repercussions on our climate and daily lives.
Influence on Global Climate
The jet stream is vital in distributing heat and moisture globally, thereby affecting climate. Major alterations to the jet stream could lead to disruptions in existing climatic conditions, resulting in shifts in precipitation and more extreme temperature variations.
Increased Variability
Some predictive models suggest that climate change may enhance the variability of the jet stream, complicating weather forecasts. Such changes could result in more erratic weather patterns.
Regional Impacts
Transformations in the jet stream could significantly affect regional climates, weather, and agricultural practices. For instance, areas may witness changes in rainfall patterns, water availability, and an uptick in extreme weather events.
Final Thoughts: The Jet Stream's Vital Role
The jet stream is a rapidly moving band of winds in the upper troposphere, formed by temperature differences between air masses. Its effects are far-reaching, influencing aviation, wind energy production, weather patterns, and overall climate. Seasonal shifts play a significant role in its dynamics, and any substantial changes to the jet stream could lead to disruptions in climate patterns, increased weather variability, and regional repercussions for agriculture and water supply.
If you've ever flown, chances are you've experienced the jet stream's influence firsthand. Thank you for engaging with this exploration of one of Earth's most fascinating atmospheric phenomena!
Witness the astonishing achievement of a new land speed world record powered by wind, showcasing the incredible force of nature.
Discover which planet in our solar system boasts the fastest wind speeds, revealing the astonishing dynamics of planetary atmospheres.